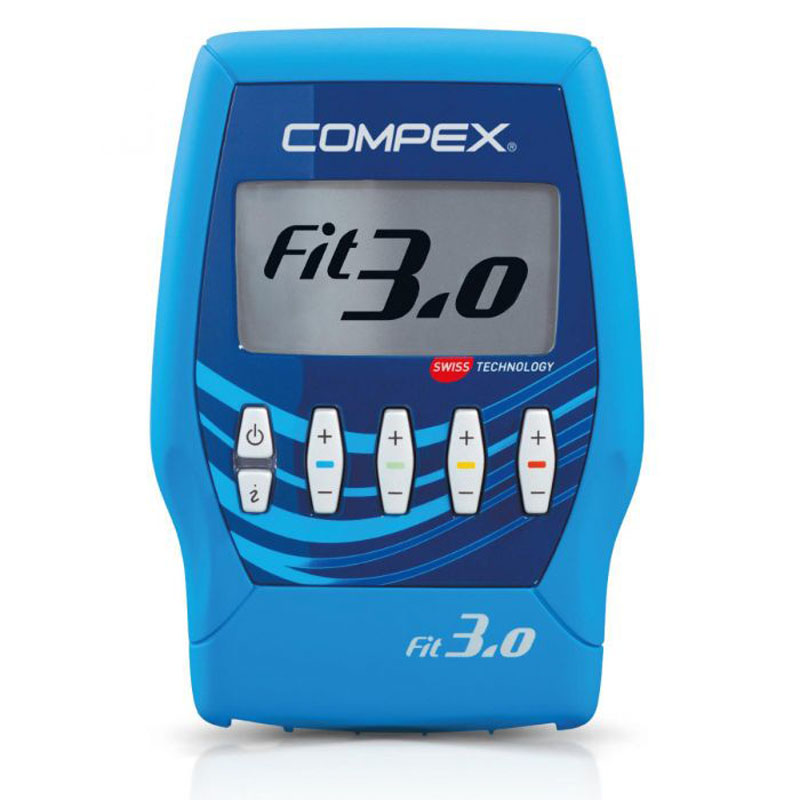
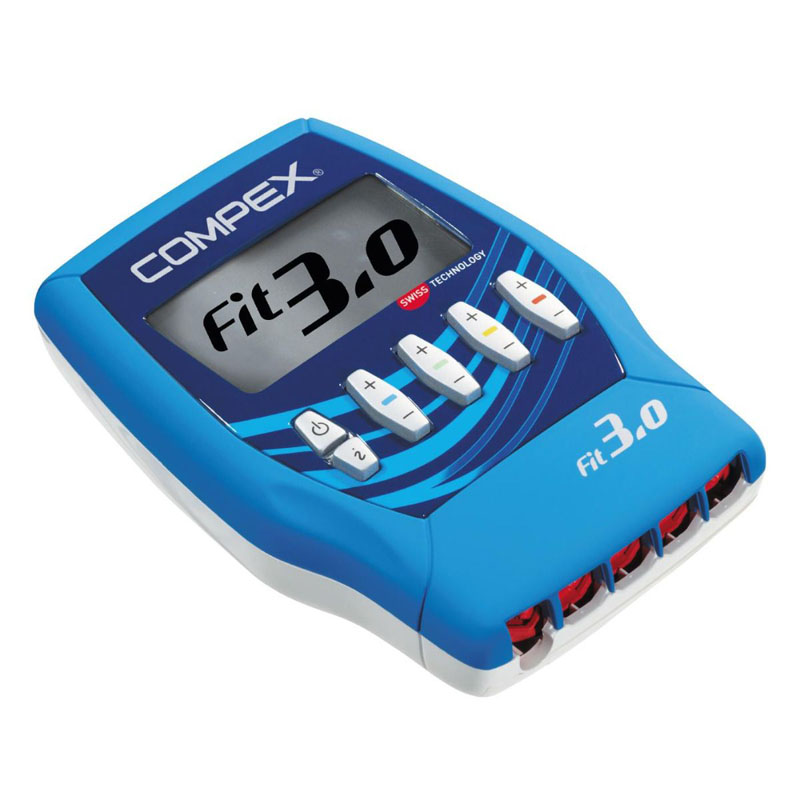
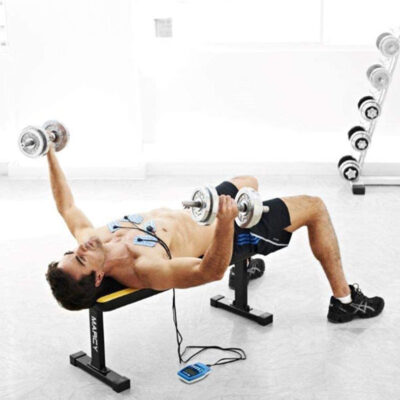
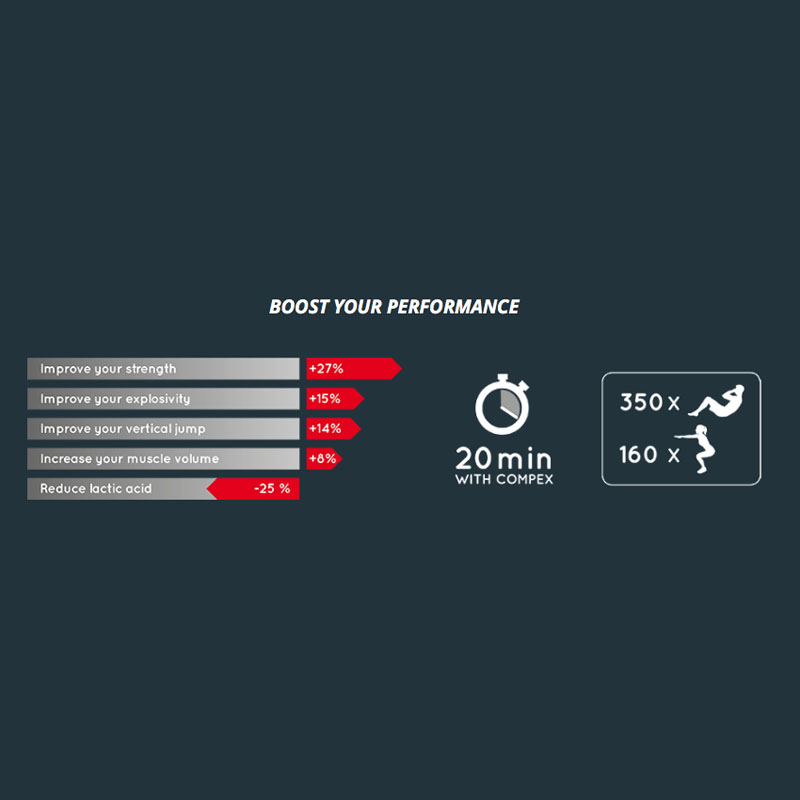
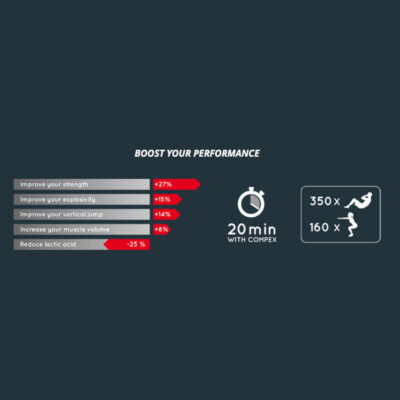
Using an electrical muscle stimulation machine can help restore strength and muscle tone while relieving pain. Including all the features of Fit 1.0 and Mi technology, Fit 3.0 also offers massage programs for fitness fans who practice their activity 3 times a week.
Including all the features of Fit 1.0 and Mi technology, Fit 3.0 also offers massage features for fitness fans who workout 3 times a week. Equipped with unique MI (muscle intelligence) technology, Compex stimulators adapt to each of your muscles to provide the most effective muscle stimulation possible, while offering greater comfort and better performance. With MI-Scan – Scans the muscle and automatically adjusts stimulator parameters to your physiology.
Compex Fit 3.0 Specifications
- Technology: Wire
- Muscle intelligence: MI-scan
- Web connection: No
- Download objective: No
- Upload remote history: No
- Program categories: Fitness, Pain management, Recovery / Massage, Rehabilitation
- NB of programs: 20
- NB of channels: 4
- Screen: Matrix monochrome
- Power: 120 mA, 400 us, 150 Hz
- Energy: Rechargeable battery in less than 4h30
What’s in the Box
- Stimulator
- Set of 4 Snap wires
- MI-Sensor wire
- Charger
- 4 Snap electrodes 5×10 cm
- 8 Snap electrodes 5×5 cm
- Transport case
- Instruction manual
Compex fit 3.0 Indications
- Fitness: Firm your arms
- Tone your thighs
- Get a 6-pack
- Build your pecs
- Firm your stomach
- Shape your buttocks
- Muscle building
- Capillarization Lymphatic drainage
- Recovery/Massage: Relaxing massage, Reviving massage
- Pain management: Pain management TENS
- Reduce muscle tension
- Muscle pain
- Neck pain
- Back pain
- Tendinitis
- Heavy legs
- Cramp prevention
- Rehabilitation: Muscle atrophy
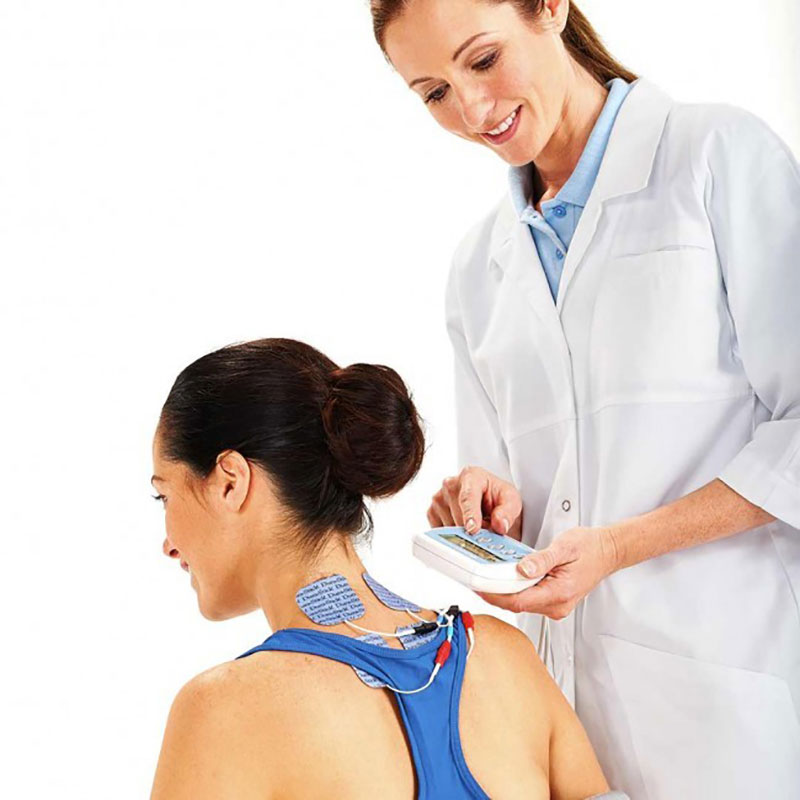
Placement of electrodes for electrical muscle stimulation
It is important to select appropriately sized electrodes (small or large) and to position them correctly on the muscle group that you wish to stimulate in order to ensure effective treatment. It is therefore appropriate to always use the electrode size shown in the illustration. If necessary, try to find the best position possible by moving the electrode on the muscle, until you locate the poin that produces the best contraction, or the greatest comfort is found.
For TENS type programes, the general rule is to cover the painful area with electrodes.
N.B. Approximate positioning of electrodes makes the session less effective, but is not dangerous.
To view the different ways of placing the electrodes, please reference the documents. For stimulation with the Mi-sensor system, all the suggested placements represent the optimal positioning of this system. It is therefore recommended that you follow these instructions. If you do not want to use Mi- technology, all you need to do is to replace the special electrode cable of the Mi-sensor system with another standard electrode cable.
Body position during electrical muscle stimulation
This position varies according to the muscle group that you wish to stimulate and the program that you are using.
For programs inducing powerful muscular contractions (tetanic contractions), it is recommended to stimulate the muscle isometrically. You should therefore hold the extremities of limbs being stimulated. This position opposes maximum resistance to movement and avoids any shortening of the muscle during contraction, which would risk causing cramps. For example, when stimulating the quadriceps, you should be in a sitting position with ankles held to avoid extending the knees.
For the other types of programs which do not induce powerful muscular contractions but only muscular twitches or tingling, position yourself as shown on the illustration, maintaining a comfortable position.
Adjusting stimulation intensities
On a stimulated muscle, the number of fibres used depends on the stimulation intensity.
For programs inducing powerful muscular contractions (tetanic contractions), you must use the maximum stimulation intensities (up to 999) while remaining within your tolerance threshold, in order to
use the maximum number of fibres. The progress of a muscle will be greater the higher number of fibres that are worked. During a session it is therefore important to try to increase the intensity every 3 to 5 contractions.
For other types of programs like recovery, massage, capillarization or even muscle pain which only induce muscle twitches, you should gradually increase the stimulation intensities until clearly visible muscle twitches are obtained.
For TENS, Epicondylitis and Tendinitis programs, you should gradually increase the intensities until you feel a tingling sensation under the electrodes.
Scheduling of electrical muscle stimulation sessions
The question of the scheduling of the stimulation sessions during the week only arises in situations where at least two training sessions are to be done in the same week.
In cases where up to six sessions a week are planned, it is recommended that the sessions be scheduled as far apart as possible. For example, anyone who does three sessions a week should do them at the rate of one session every two days (2×1 rest day and 1×2 days of rest/week). Anyone who does six sessions should do six consecutive days of stimulation with one day of rest.
Above seven sessions a week, it is advisable to group several sessions together on the same day to leave yourself one or two complete rest days without stimulation. Anyone who does seven sessions a week should do five days of stimulation, at the rate of one session per day with one two-session day(s) (with at least a half-hour’s rest between the sessions), leaving one rest day. Anyone who does ten sessions a week should preferably do five two-session days (again with at least a half-hour’s rest between the sessions), leaving two rest days.
Alternation of stimulation sessions/voluntary training
The stimulation sessions can be done outside of or during voluntary training.
When voluntary training and stimulation are done during the same session, it is generally recommended that the voluntary training be done first followed by the stimulation. This means that the voluntary training is not done on muscle fibres which are already tired. This is particularly important for strength and explosive strength training.
However, in resistance training, it can be very useful to proceed in the reverse order. Before the voluntary training, by means of stimulation for resistance, a “specific pre-fatigue session” is carried out on the muscle fibres without general and cardio-vascular fatigue. In this way, the voluntary effort on the “prepared” fibres will push the glycolytic metabolism faster and further.
Progression of electrical muscle stimulation cycles
The stimulation cycles are for people who are already accustomed to electrostimulation and want to perform several training cycles.
The cycle logic refers to the workload performed by electrostimulation. Just like a normal workout, one has to to start with an amount of effort then increase it over the course of the cycles. Thus, it is recommended starting with the 1st cycle and going on to the next level when the cycle is finished, normally after 4 to 6 weeks of stimulation based on 3 sessions per week.
It is also important to have reached significant stimulation intensities in sessions before going on to another cycle. At the end of a cycle you can either start a new cycle or do maintenance training based on one session per week.
Documents
 Compex Quick Start Guide
Compex Quick Start Guide
 Instructions for Use
Instructions for Use
 Electrode Placement Diagram
Electrode Placement Diagram
Videos











 Ask A Question
Ask A Question
 Tax Exempt Shopping
Tax Exempt Shopping
 Get Clinical Pricing
Get Clinical Pricing
 Affiliate Program
Affiliate Program
 Retail Stores
Retail Stores
 Health Hub
Health Hub
 Shipping Policy
Shipping Policy
 Returns/Exchanges
Returns/Exchanges
 About Us
About Us
 Contact Us
Contact Us



 BIOFLEX P120 Light Therapy System
BIOFLEX P120 Light Therapy System




































Reviews
There are no reviews yet